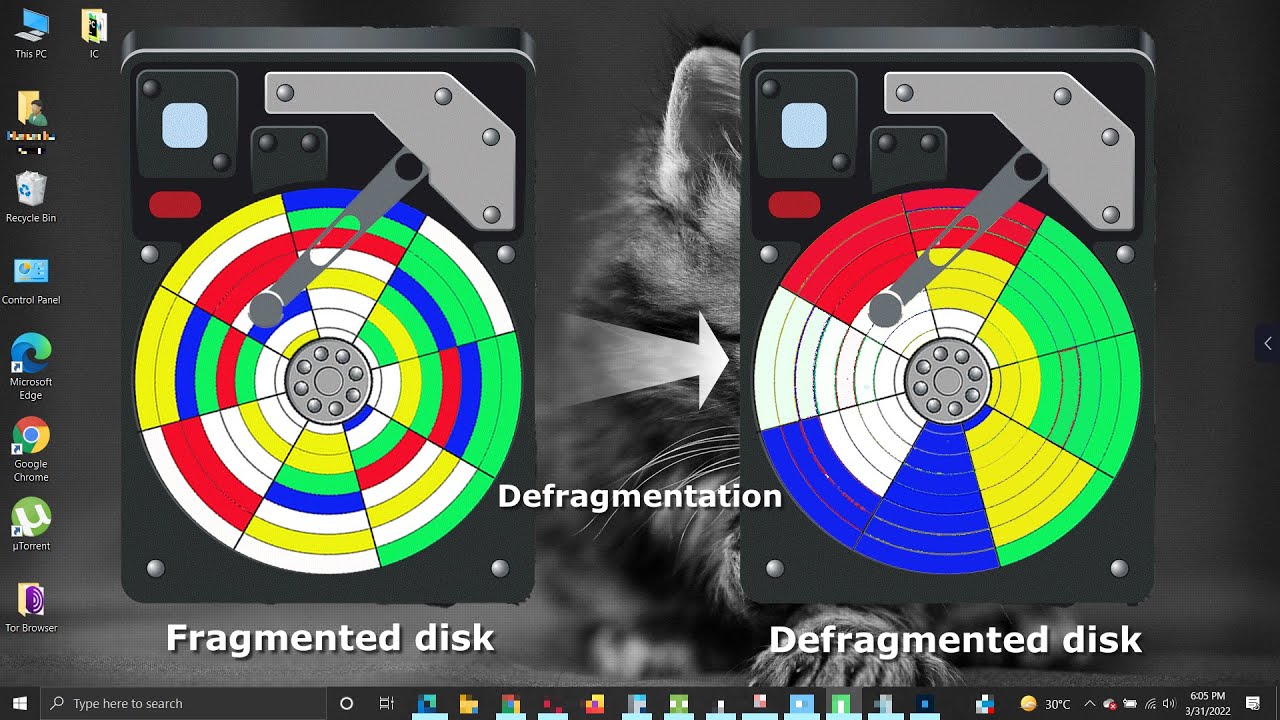
Disk defragmentation is the process of consolidating fragmented files on a computer’s hard drive. When files are stored in fragmented pieces across the disk, it can slow down the system’s performance because the read/write heads have to move more to access these pieces. Defragmentation helps organize these files to be contiguous, thereby improving system performance.
How to Perform Disk Defragmentation on Windows
- Open Disk Defragmenter:
- Press
Windows + Sto open the search bar. - Type Defragment and Optimize Drives and select it from the search results.
- Press
- Select the Drive to Defragment:
- In the Optimize Drives window, you’ll see a list of all available drives on your computer.
- Select the drive you want to defragment (typically the
C:drive).
- Analyze the Drive:
- Click Analyze to check if the drive needs defragmentation. The tool will display the percentage of fragmentation. If it’s above 10%, it’s a good idea to proceed with defragmentation.
- Defragment the Drive:
- Click Optimize to begin the defragmentation process. This can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the size and fragmentation level of the drive.
- Wait for the Process to Complete:
- Allow the process to finish. You can continue to use your computer during defragmentation, but performance may be slower.
- Schedule Regular Defragmentation (Optional):
- You can set up a schedule for regular defragmentation. Click on Change settings and select the frequency (e.g., weekly or monthly) to automate this process.
Additional Tips
- SSDs vs. HDDs: If you have a Solid State Drive (SSD), you do not need to defragment it. SSDs use flash memory, and defragmenting them can actually reduce their lifespan. Instead, you can optimize your SSD using Windows’ built-in tools.
- Third-party Tools: Some third-party tools like Defraggler or Auslogics Disk Defrag offer additional features and might provide more control over the defragmentation process.
- Free Up Space: Before defragmenting, ensure you have some free space on your hard drive (at least 15% of the total drive capacity) to allow the defragmenter to move files around efficiently.
By regularly performing disk defragmentation on traditional hard drives, you can maintain and even improve your system’s performance over time.