Here’s a beginner-friendly guide to help you understand:
🧰 How to Use Git and GitHub for Version Control
Whether you’re building a website, mobile app, or working with a team, version control is essential to keep track of changes and collaborate smoothly. That’s where Git and GitHub come in.
🔄 What Is Version Control?
Version control lets you:
- Track changes in your code over time
- Revert to previous versions if something breaks
- Work with others without overwriting each other’s work
🐙 What Is Git?
Git is a local version control system. It tracks changes in your project on your computer.
☁️ What Is GitHub?
GitHub is a remote hosting platform for Git repositories. It allows you to:
- Back up your code online
- Share projects publicly or privately
- Collaborate with others (pull requests, issues, etc.)
- Show off your portfolio
✅ What You Need
- Install Git
- Create a free GitHub account
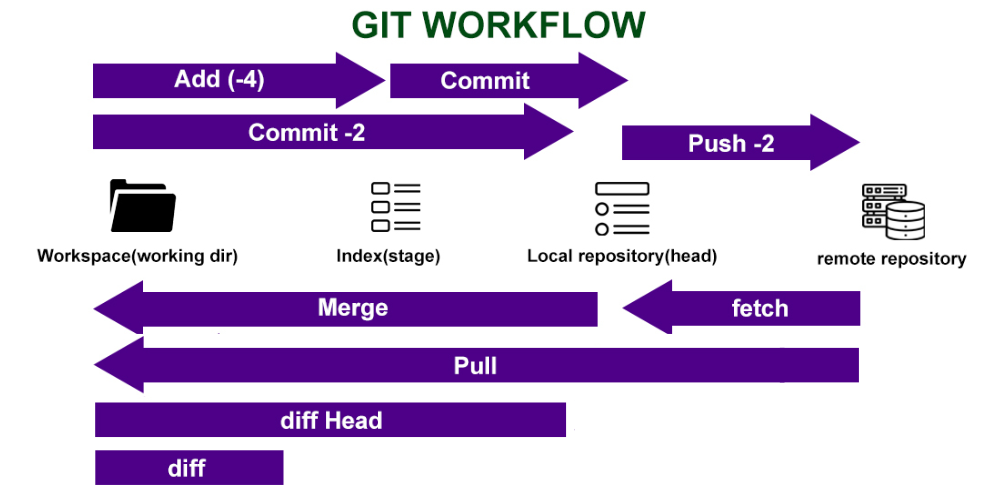
🔧 Basic Git Workflow
1. Create a Project Folder
mkdir my-project
cd my-project
2. Initialize Git
git init
This creates a .git folder to track your changes.
3. Track Files
Create a file like index.html, then:
git add index.html
Or add everything:
git add .
4. Commit Your Changes
git commit -m "Initial commit"
This saves a snapshot of your code.
5. Connect to GitHub
First, create a new repo on GitHub (don’t add README).
Then, link your local repo:
git remote add origin https://github.com/yourusername/my-project.git
Push your code to GitHub:
git push -u origin main
(If your branch is master, use master instead of main.)
🔁 Basic Git Commands Cheat Sheet
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
git init |
Start tracking a new project |
git status |
See changes and staging info |
git add . |
Stage all changes |
git commit -m "message" |
Save a version |
git log |
View commit history |
git remote add origin [url] |
Connect to GitHub |
git push / git pull |
Sync with GitHub |
git clone [repo-url] |
Copy someone’s GitHub repo |
git branch |
View branches |
git checkout -b new-branch |
Create & switch to a new branch |
git merge branch-name |
Combine another branch into current |
🌿 Branching Example
Branching helps you experiment without affecting the main code.
git checkout -b new-feature
Work on your feature, then:
git add .
git commit -m "Add new feature"
git checkout main
git merge new-feature
👥 Collaboration: Pull Requests
On GitHub, when someone makes a change, they can open a Pull Request (PR) to propose it.
Steps:
- Fork a repo
- Make changes in a new branch
- Push to your fork
- Open a Pull Request on GitHub
- Discuss and merge
🔐 .gitignore File
Create a .gitignore file to prevent committing unwanted files:
node_modules/
.env
*.log
🧠 Tips for Beginners
- Make frequent commits with meaningful messages
- Use branches to test features
- Push your projects to GitHub to build a portfolio
- Use GitHub Issues to manage tasks
📚 Learn More
- GitHub Docs
- Git Handbook (GitHub)
- Learn Git Branching (visual practice)
- YouTube: “Git & GitHub Crash Course” by Traversy Media or freeCodeCamp
🎯 Final Thought
Using Git and GitHub not only helps you manage your code better but also shows professionalism in your development work. It’s one of the most valuable skills for developers at any level.