How to Connect a Website to a Database
Here’s a step-by-step beginner-friendly guide using PHP + MySQL, which is one of the most common and easiest setups for small to medium-sized websites.
✅ 1. What You Need
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Website Files | HTML/CSS/JS for structure and design |
| Backend Code | PHP or Node.js to process logic |
| Database | MySQL or similar to store data |
| Web Server | Apache or Nginx to host the site |
| Hosting | Local (XAMPP/WAMP) or online hosting |
🧰 For beginners, using XAMPP (includes PHP, MySQL, Apache) is the easiest way to start locally.
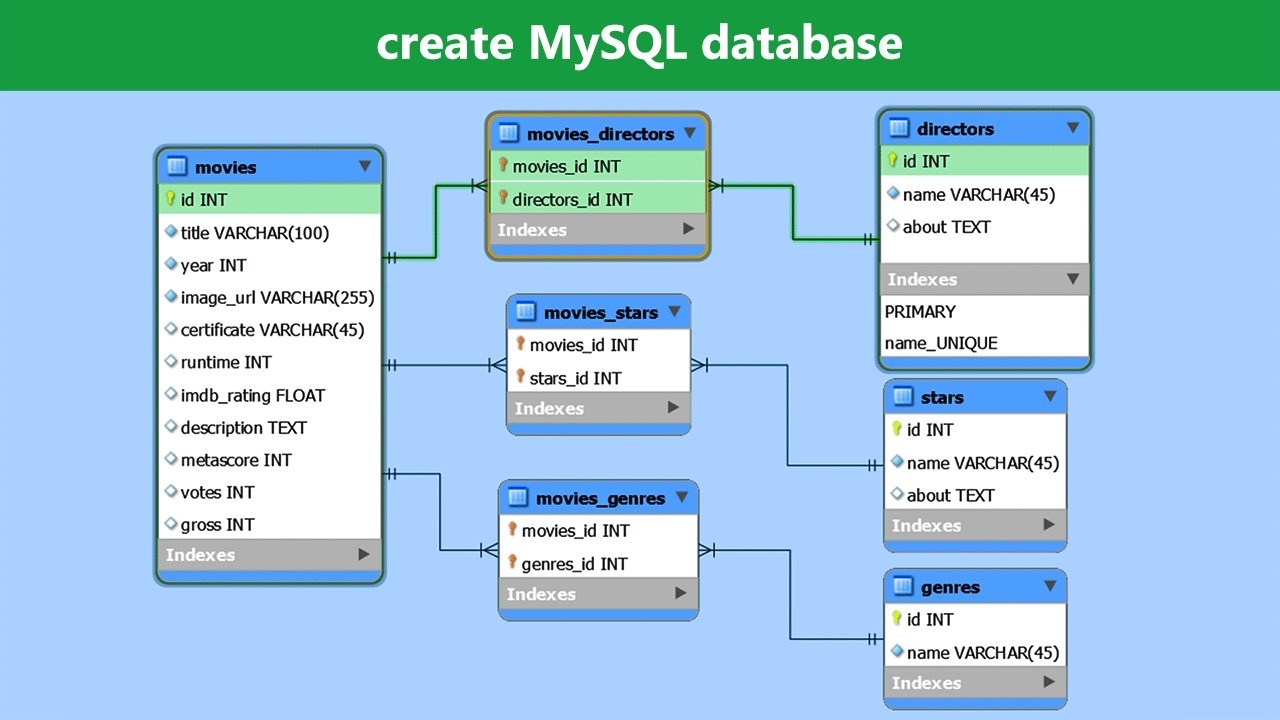
✅ 2. Create the Database
Using phpMyAdmin (comes with XAMPP):
- Go to
http://localhost/phpmyadmin - Click Databases
- Enter a name (e.g.,
mywebsite) - Click Create
- Create a table (e.g.,
users) with fields like:id(INT, AUTO_INCREMENT)name(VARCHAR)email(VARCHAR)
✅ 3. Write PHP to Connect to the Database
Create a file called connect.php:
<?php
$host = "localhost"; // Server name
$user = "root"; // Default user for XAMPP
$pass = ""; // Default password (empty)
$dbname = "mywebsite"; // Database name
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($host, $user, $pass, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
}
echo "Connected successfully!";
?>
✅ Save it in the
htdocsfolder (e.g.,C:\xampp\htdocs\connect.php)
Then go to http://localhost/connect.php in your browser.
✅ 4. Insert or Fetch Data
📥 Insert Data Example:
$sql = "INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ('John Doe', 'john@example.com')";
if ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) {
echo "New record created successfully!";
} else {
echo "Error: " . $conn->error;
}
📤 Fetch Data Example:
$sql = "SELECT * FROM users";
$result = $conn->query($sql);
while($row = $result->fetch_assoc()) {
echo "Name: " . $row["name"] . " | Email: " . $row["email"] . "<br>";
}
🧠 How It Works
- HTML sends data (via a form)
- PHP processes it and connects to the database
- SQL statements (
INSERT,SELECT,UPDATE,DELETE) interact with the database - Results are sent back to the user as HTML
🔐 Security Tips
- Always sanitize user inputs to avoid SQL injection
- Use prepared statements with
mysqlior PDO
- Use prepared statements with
- Use HTTPS in production
- Never expose database credentials publicly
🔁 Alternative Stack Examples
| Tech Stack | Language | Database |
|---|---|---|
| LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP) | PHP | MySQL |
| MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js) | JS | MongoDB |
| Django | Python | PostgreSQL or SQLite |
| Ruby on Rails | Ruby | PostgreSQL or SQLite |
📚 Free Tools to Practice
🚀 Final Thought
Connecting a website to a database opens the door to building interactive, user-driven applications like blogs, shops, login systems, and more.