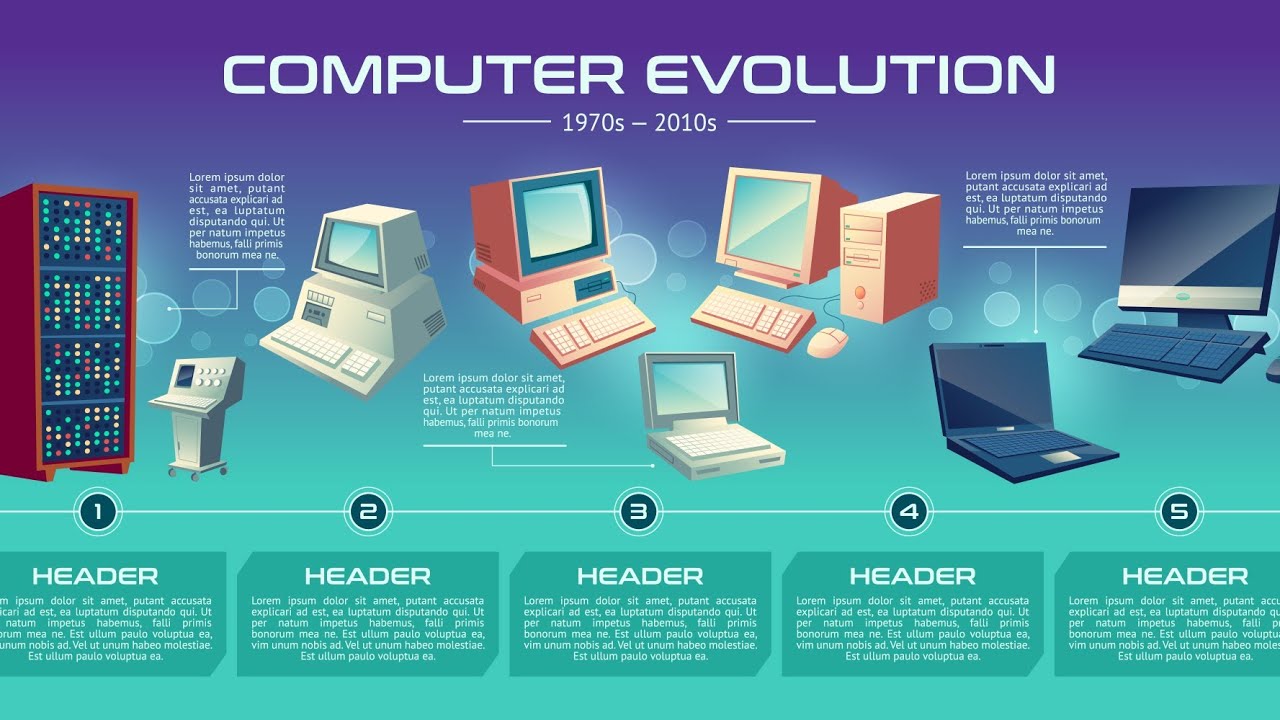
The Evolution of Computers: From ENIAC to AI-Powered Systems
Computers have come a long way from the massive, room-sized machines of the 1940s to the sleek, AI-powered systems we use today. Their evolution has been driven by advancements in technology, making them smaller, faster, and more intelligent. This article explores the journey of computers, from the early days of the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) to the present era of artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum computing.
1. The First Generation (1940s – 1950s): The Birth of Computers
ENIAC – The First General-Purpose Computer
The ENIAC, developed in 1945 by John Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, was the world’s first general-purpose electronic computer. It was:
✔ Huge – Occupied 1,800 square feet and weighed 30 tons.
✔ Slow by today’s standards – Performed 5,000 additions per second.
✔ Used vacuum tubes – About 18,000 vacuum tubes for processing.
🔹 Other notable first-generation computers:
- UNIVAC I (1951): First commercial computer.
- IBM 701 (1952): First IBM scientific computer.
2. The Second Generation (1950s – 1960s): The Transistor Revolution
In the late 1950s, transistors replaced vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, more efficient, and less expensive.
🔹 Key improvements:
- Transistors were faster, more reliable, and energy-efficient.
- Computers were smaller and less prone to overheating.
- Introduced magnetic core memory for better storage.
Examples:
- IBM 1401 (1959): One of the most popular business computers.
- CDC 1604 (1958): First supercomputer using transistors.
3. The Third Generation (1960s – 1970s): The Rise of Integrated Circuits
🔹 The invention of the integrated circuit (IC) in 1958 by Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce was a game-changer.
✨ Key advancements:
- ICs combined multiple transistors on a single chip, making computers even smaller and more powerful.
- Introduced keyboards and monitors (instead of punched cards).
- Allowed mass production, reducing costs.
Examples:
- IBM System/360 (1964): Used in businesses and government.
- DEC PDP-8 (1965): One of the first minicomputers.
4. The Fourth Generation (1970s – 1980s): The Birth of Microprocessors & Personal Computers
🔹 The microprocessor, introduced by Intel in 1971 (Intel 4004), marked the beginning of modern computing.
✨ Key changes:
- Microprocessors integrated the CPU on a single chip.
- Computers became affordable and available for personal use.
- Introduction of Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs), keyboards, and mice.
💻 The Rise of Personal Computers (PCs):
- Apple I & II (1976-77): Created by Steve Jobs & Steve Wozniak.
- IBM PC (1981): Set the standard for modern PCs.
- Microsoft Windows (1985): First GUI-based OS.
5. The Fifth Generation (1990s – Present): AI, Cloud Computing & Smart Devices
🔹 This era is marked by artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and supercomputers.
🚀 Key breakthroughs:
- The rise of the Internet & World Wide Web (WWW) in the 1990s.
- The development of supercomputers, like IBM’s Deep Blue (defeated chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997).
- AI-powered devices like Google Assistant, Alexa, and Siri.
- Advancements in quantum computing and neural networks.
💡 Modern Supercomputers & AI:
- IBM Watson: AI that competes with humans in quizzes.
- GPT-4 (by OpenAI): Advanced AI for text processing.
- Google DeepMind: AI solving complex scientific problems.
6. The Future: Quantum Computing & AI Dominance
The future of computers is heading toward quantum computing, AI automation, and even brain-computer interfaces (BCI).
🔮 Predictions:
- Quantum computers like Google’s Sycamore will solve problems that classical computers can’t.
- AI will continue evolving, impacting industries from healthcare to finance.
- Holographic and wearable computers may replace traditional screens.
Conclusion
From ENIAC’s vacuum tubes to AI-driven quantum computers, the evolution of computers has transformed the world. Each generation has redefined speed, efficiency, and accessibility, paving the way for even more advanced technologies in the future.






Appreciating the hard work you put into your website and in depth information you offer.
It’s awesome to come across a blog every once in a while that
isn’t the same old rehashed material. Excellent read!
I’ve saved your site and I’m including your RSS feeds to my Google account.
Hey there, You have done an incredible job.
I will definitely digg it and personally suggest to
my friends. I’m sure they will be benefited from this site.
Wonderful article! That is the type of information that are meant to be shared around the
web. Disgrace on Google for not positioning this post higher!
Come on over and talk over with my web site . Thanks